For 1990-2009 cars only
As vehicle speed increases further, and when other input signals to the TCM are appropriate, the TCM de-energizes the 1-2/3-4 shift solenoid to shift the transmission into Fourth gear.
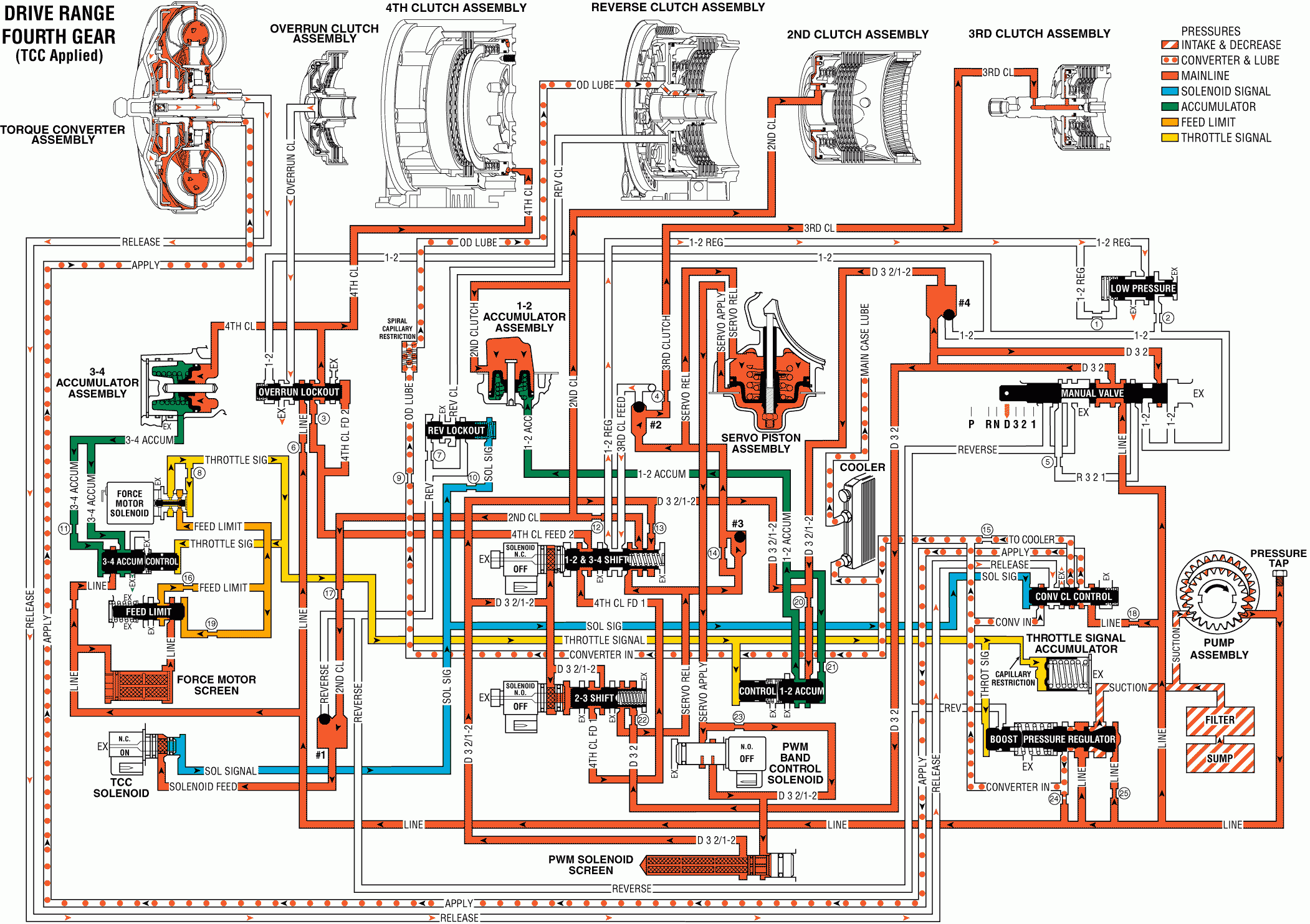
2-3 Shift Solenoid: De-energized (OFF) as in Third gear, the solenoid is open. D32/1-2 fluid flows through the solenoid and acts on the end of the 2-3 shift valve.2-3 Shift Valve: D32/1-2 fluid pressure from the 2-3 shift solenoid keeps the 2-3 shift valve shifted against spring force and in the Third and Fourth gear position. D32/1-2 fluid continues to fill the 4th clutch feed 1 fluid circuit and orificed D32 fluid continues to fill the servo release fluid circuit.
1-2/3-4 Shift Solenoid: De-energized (turned OFF) by the TCM, the solenoid is closed and blocks D32/1-2 fluid pressure from passing through the solenoid and acting on the 1-2/3-4 shift valve. D32/1-2 fluid at the solenoid end of the 1-2/3-4 shift valve exhausts through the end of the solenoid.
1-2/3-4 Shift Valve: With D32/1-2 fluid pressure from the shift solenoid exhausted, spring force moves the valve toward the solenoid and into the First and Fourth gear position. In this position the following changes occur at the shift valve:
| • | 4th clutch feed 1 fluid fills the 4th clutch feed 2 fluid circuit. |
| • | Orificed D32/1-2 fluid pressure at the spring end of the valve is blocked from feeding the 2nd clutch fluid circuit and assists spring force on the valve. |
| • | Servo release fluid is blocked from feeding the 3rd clutch feed fluid circuit. 3rd clutch feed fluid exhausts through the valve, into the 1-2 regulated fluid circuit and past the low pressure control valve. |
| • | Servo release fluid is routed into the 2nd clutch fluid circuit to keep the 2nd clutch and TCC applied in Fourth gear. |
Overrun Clutch Releases And 4th Clutch Applies
Overrun Lockout Valve: 4th clutch feed 2 fluid pressure shifts the valve against spring force and into the Fourth gear position. In this position the following changes occur:| • | Line pressure is blocked from entering the overrun clutch fluid circuit and overrun clutch fluid is open to an exhaust port at the valve. |
| • | Orificed 4th clutch feed 2 fluid at the middle of the valve fills the 4th clutch fluid circuit. |
4th Clutch Piston: 4th clutch fluid pressure moves the piston to apply the 4th clutch plates and obtain Fourth gear.
3-4 Accumulator Piston: 4th clutch fluid pressure moves the piston against spring force and 3-4 accumulator fluid pressure. This action absorbs initial 4th clutch fluid pressure to cushion the 4th clutch apply. Also, the movement of the accumulator piston forces some 3-4 accumulator fluid out of the accumulator assembly.
3-4 Accumulator Valve Train: Regulates the exhaust rate of excess 3-4 accumulator fluid past the 3-4 accumulator valve (407). This fluid regulation is controlled by orificed accumulator fluid pressure moving the valve train against throttle signal fluid pressure acting on the 3-4 accumulator control valve (409).
Checkball #2: With 3rd clutch fluid exhausted, servo release fluid pressure seats the ball against the 3rd clutch feed fluid circuit. Only servo release fluid feeds the 3rd clutch fluid circuit in Fourth gear.
Converter Clutch
TCC Solenoid: The TCC solenoid is ON and the converter clutch applied. Under normal operating conditions the TCC will be applied in Fourth gear.Important: Remember that the TCC releases during all upshifts and downshifts, re-applying after the shift is complete if operating conditions are appropriate.
Overdrive Range, Fourth Gear - TCC Applied