Front Disc Brake Pads Replacement Without J55
Removal Procedure
- Remove two-thirds of the brake fluid from the master cylinder.
- Raise the vehicle and suitably support. Refer to Lifting and Jacking the Vehicle in General Information.
- Mark the relationship of the wheel to the axle flange.
- Remove the Wheel. Refer to Tire and Wheel Removal and Installation in Tires and Wheels.
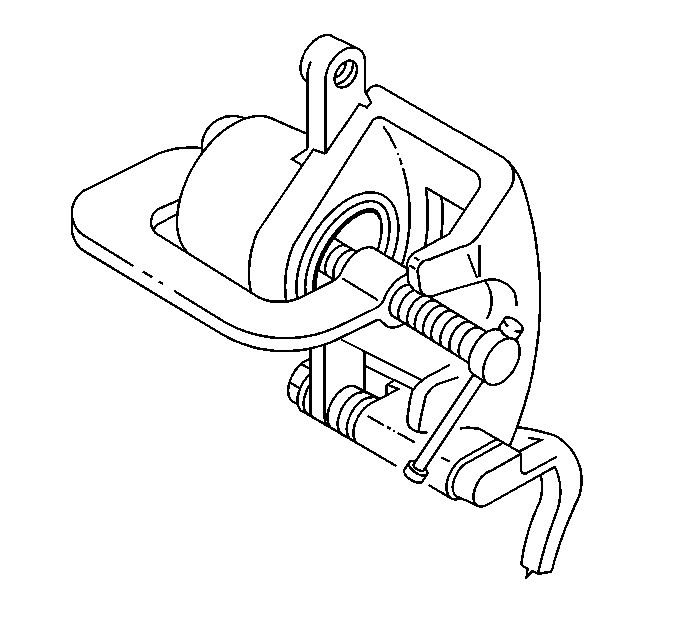
- Using a large C clamp compress the caliper piston into the caliper bore completely.
- Remove the caliper slide pins.
- Remove the caliper from the anchor and support.
- Remove the inboard and outboard pads from the anchor bracket.
- Remove and inspect the pad retainers.
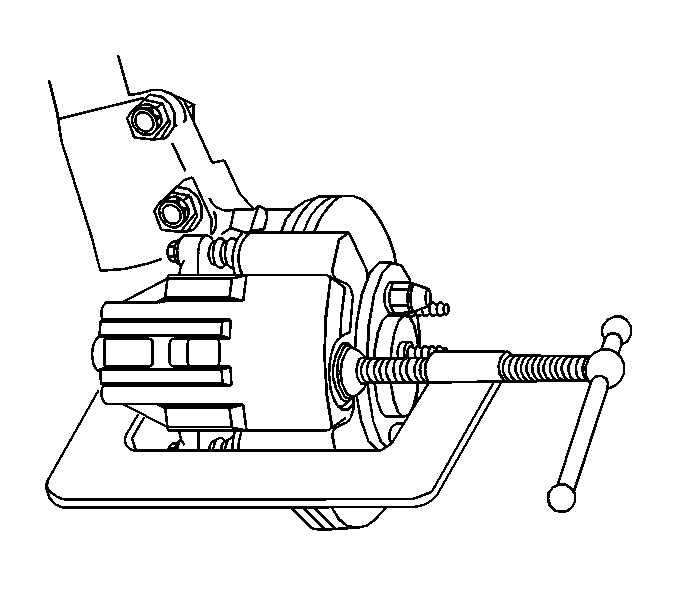
Important: Do not use a screwdriver or pry bar to compress the caliper piston into the caliper. Any damage to the piston boot could cause corrosive elements to enter the piston sealing area and lead to the piston seizing in the caliper bore.

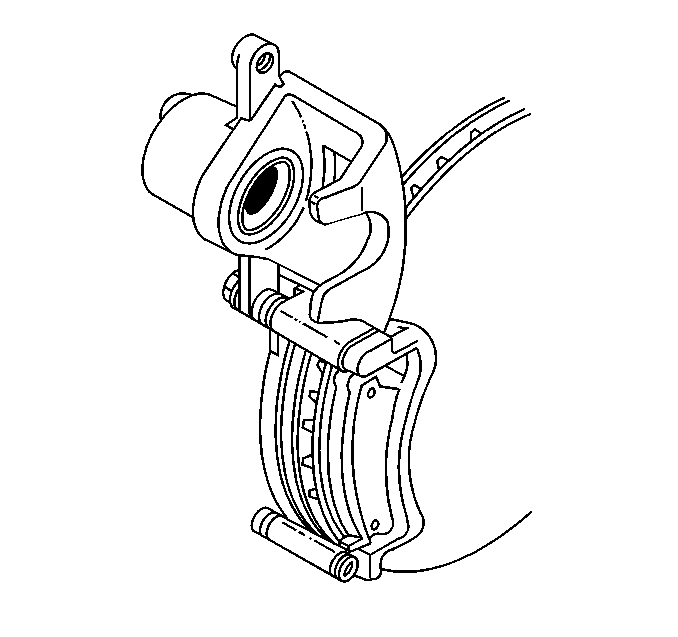
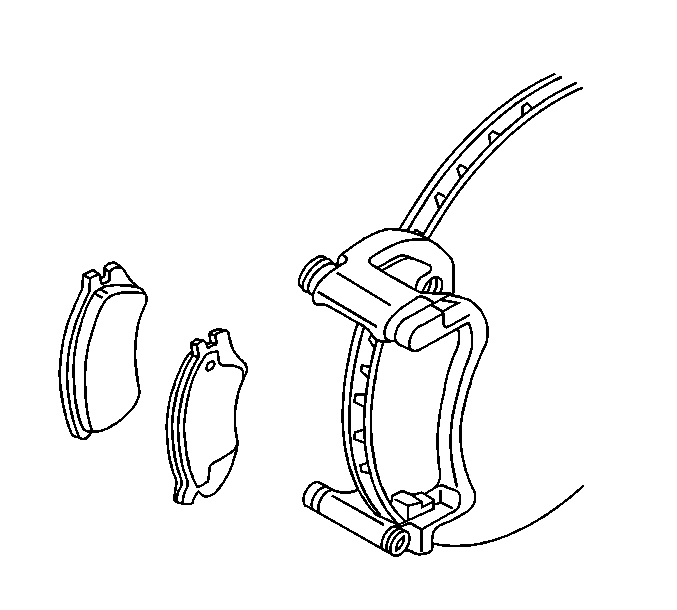
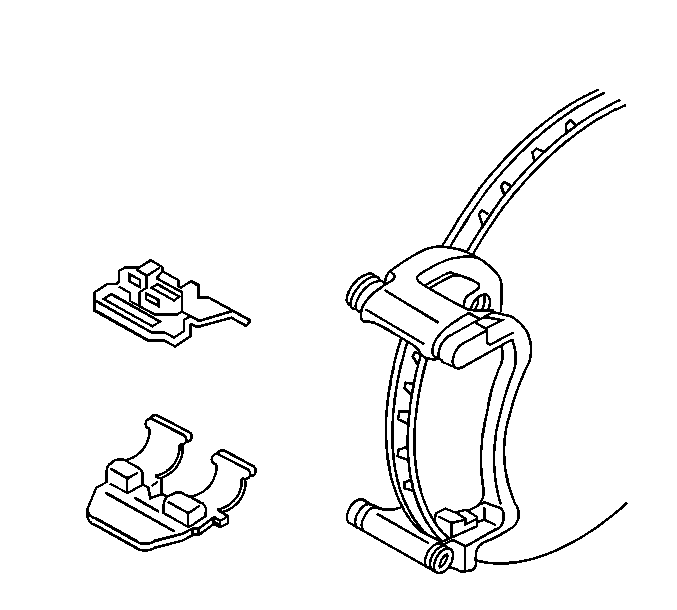
Important: Inspect the caliper bolt suspension boots for cuts, tears, or deterioration. If damaged, replace the pin boots. Refer to Brake Caliper Bracket Overhaul . Inspect the piston boot for deterioration. If damaged, Refer to Front Brake Caliper Overhaul . Inspect the caliper pin bolt for damage or corrosion. Replace if damaged or corroded. Do not attempt to clean away corrosion. Corrosion is typically caused by damaged pin boots.
Installation Procedure
- Install the brake pad retainers into the caliper anchor bracket.
- Install both brake pads into the caliper anchor bracket.
- If new brake pads are being installed in the vehicle it may be necessary to bottom the caliper piston completely into the caliper bore. Use a large C clamp and compress the piston into the caliper bore.
- Use a small plastic or wooden tool (1) to lift the inner edge of the boot next to the piston (2), and press out any trapped air.
- Install the caliper down over the brake pads and onto the anchor bracket.
- Insert the caliper slide pins.
- Install the tire and wheel assembly. Refer to Tire and Wheel Removal and Installation in Tires and Wheels.
- Lower the vehicle.
- Start the vehicle and apply approximately 778 N·m(175 lb ft.) of force three times to the brake pedal to seat the brake caliper piston and brake pads.
- Burnish the pads and rotors. Refer to Brake Pad and Rotor Burnishing .


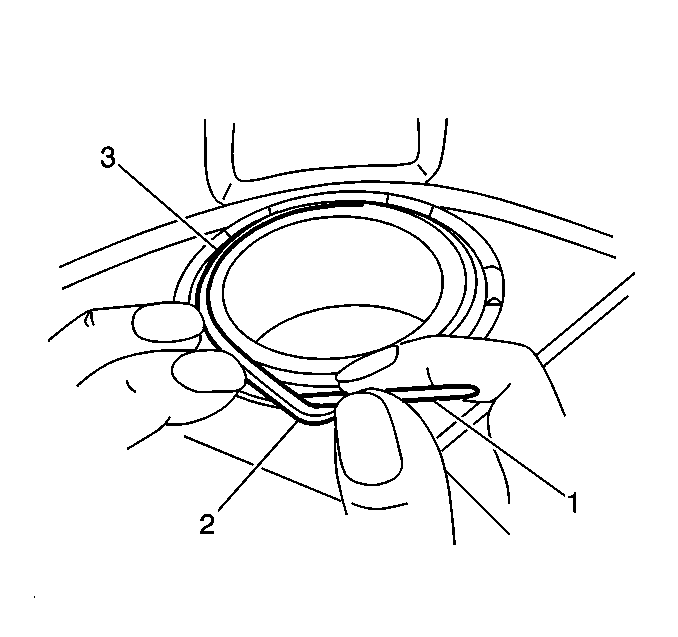
Important: The caliper piston boot must lay flat. Make sure convolutions are tucked into place.

Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
Tighten
Tighten the caliper slide pin to 85 N·m (63 lb ft).
Front Disc Brake Pads Replacement J55
Removal Procedure
- Remove two-thirds of the brake fluid from the master cylinder.
- Raise the vehicle and suitably support. Refer to Lifting and Jacking the Vehicle in General Information.
- Mark the relationship of the wheel to the axle flange.
- Remove the Wheel. Refer to Tire and Wheel Removal and Installation in Tires and Wheels.
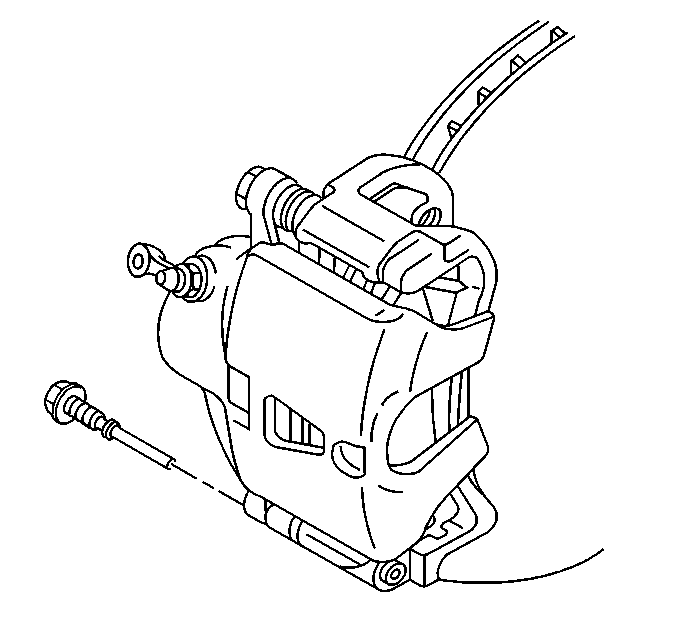
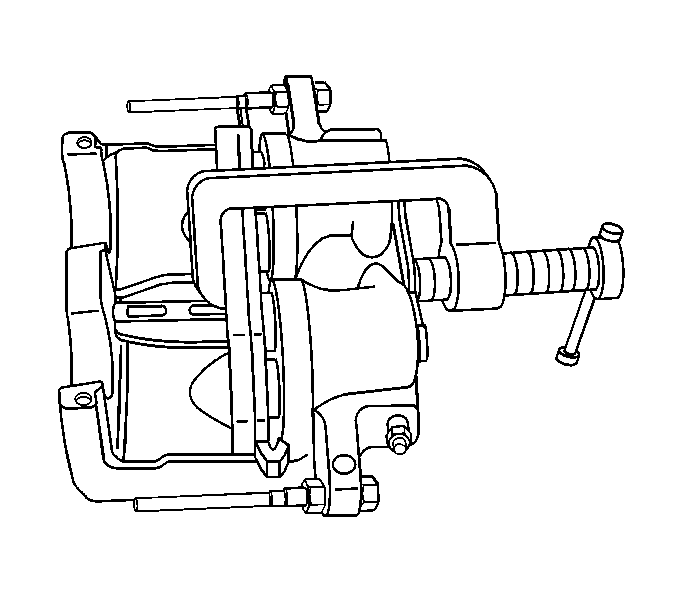
- Using a large C clamp compress the caliper pistons into the caliper bore completely.
- Remove the caliper slide pins (1).
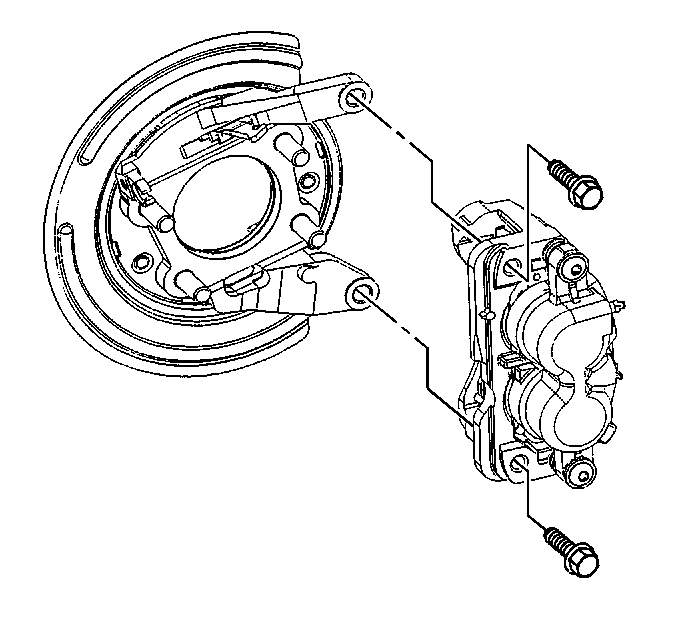
- Remove the caliper from the anchor and support.
- Remove the inboard and outboard pads from the anchor bracket.
- Remove and inspect the pad retainers.
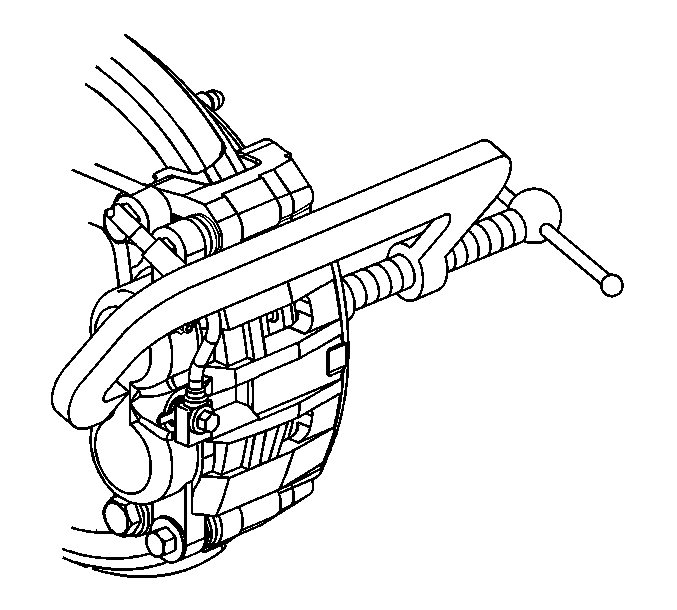
Important: Do not use a screwdriver or pry bar to compress the caliper pistons into the caliper. Any damage to the piston boots could cause corrosive elements to enter the piston sealing area and lead to the piston seizing in the caliper bores.
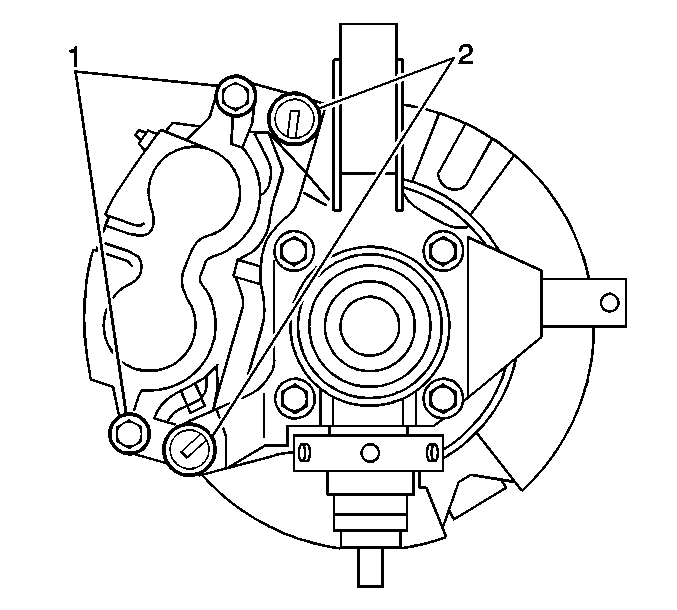
Important: Inspect the caliper bolt suspension boots for cuts, tears, or deterioration. If damaged, replace the pin boots. Refer to Brake Caliper Bracket Overhaul . Inspect the piston boot for deterioration. If damaged, Refer to Front Brake Caliper Overhaul . Inspect the caliper pin bolts for damage or corrosion. Replace if damaged or corroded. Do not attempt to clean away corrosion. Corrosion is typically caused by damaged pin boots.
Installation Procedure
- Install the brake pad retainers into the caliper anchor bracket.
- If new brake pads are being installed in the vehicle it may be necessary to bottom the caliper pistons completely into the caliper bore.
- Use a small plastic or wooden tool (1) to lift the inner edge of the boot next to the piston (2), and press out any trapped air.
- Install the caliper down over the brake pads and onto the anchor bracket.
- Insert the caliper slide pins.
- Install the tire and wheel assembly. Refer to Tire and Wheel Removal and Installation in Tires and Wheels.
- Lower the vehicle.
- Start the vehicle and apply approximately 778 N·m(175 lb ft.) of force three times to the brake pedal to seat the brake caliper piston and brake pads.
- Burnish the pads and rotors. Refer to Brake Pad and Rotor Burnishing .

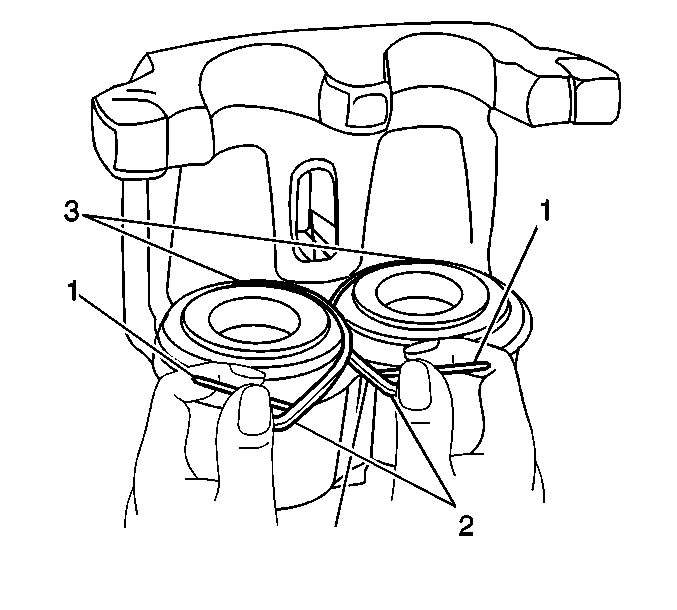
Important: The caliper piston boots must lay flat. Make sure convolutions are tucked into place.


Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
Tighten
Tighten the caliper slide pins to 85 N·m (63 lb ft).
