The compressor is a scroll compressor that matches the
air conditioning demand by changing the compressor stroke, instead of cycling
the compressor clutch. A capacity control valve located in the compressor
senses the low side pressure and causes the compressor to adjust to A/C
cooling demands. The compressor always runs and the system does not cycle.
However, the compressor may cycle if the cooling load is not reduced enough
by the capacity control valve.
Refer to the following tables when you are diagnosing insufficient cooling
complaints.
Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
1
| Inspect for any stored DTCs.
Are any DTCs stored?
| --
| Go to
Step 3
| Go to
Step 2
|
2
| Connect the J 39500-B
Are the pressures above 350 kPa (50 psi)?
| --
| Go to
Step 4
| Go to
Step 8
|
3
| Correct any stored DTCs. Refer to
Diagnostic System Check
.
Does the complaint persist?
| --
| Go to
Step 1
| System OK
|
4
| Inspect and correct for a blown Air Conditioner (A/C) fuse.
Does the complaint persist?
| --
| Go to
Step 5
| System OK
|
5
|
- Disconnect the A/C clutch connector.
- Inspect the A/C clutch for proper rotation.
Does the A/C clutch rotate smoothly?
| --
| Go to
Step 6
| Go to
Air Conditioning Compressor Replacement
|
6
| Inspect and correct for the following conditions:
Does the complaint persist?
| --
| Go to
Step 7
| System OK
|
7
|
- Read the DCS for Bulletins and Hints.
Follow the procedures indicated.
Does the complaint persist?
| --
| Go to
Step 10
| System OK
|
8
|
- Add 0.453 kg (1 lb) of refrigerant.
- Perform a leak check. Refer to Leak Testing
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
Did you find a leak?
| --
| Go to
Step 9
| Go to
Step 10
|
9
|
- Repair the leak.
- Recover and recharge the A/C system. Refer to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating,
Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
Does the complaint persist?
| --
| Go to
Step 2
| System OK
|
10
| Perform an A/C Performance Check using the following steps:
- Ensure that the ambient temperature is at least 4°C (39°F).
- Ensure that the engine is idling at normal operating temperature.
- Turn the A/C to the ON position.
- Select the coldest setting.
- Select the MAX blower speed.
- Record the A/C pressures.
- Record the A/C temperatures.
- Refer to
System Performance Test
.
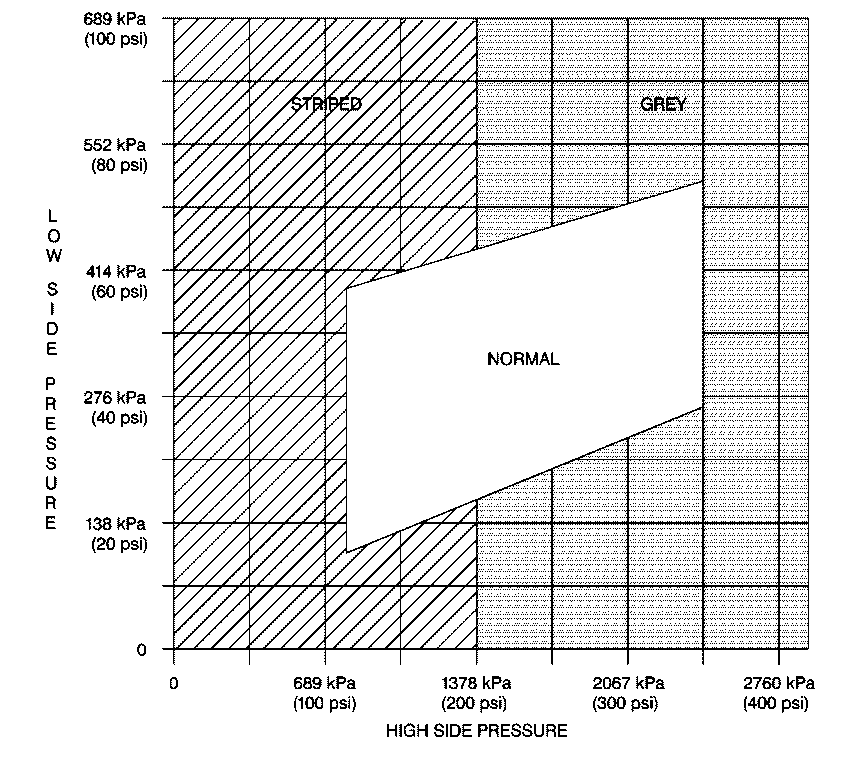
Does the A/C performance meet the requirement on the Performance Chart?
| --
| Go to
Step 11
| Go to HVAC High Side vs. Low
Side Pressure Table
|
11
| Was the customer complaint made due to high temperature
and/or high humidity?
| --
| System OK
| Go to
Step 12
|
12
| Perform a leak test. Refer to Leak Testing
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
Did you find a leak?
| --
| Go to
Step 13
| System OK
|
13
|
- Repair the leak.
- Recover and recharge the A/C system. Refer to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating,
Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
Does the complaint persist?
| --
| Go to
Step 10
| System OK
|
Gray Area Diagnosis and Service
Problem
| Action
|
|
Important: The clutch may cycle if the discharge pressure exceeds 2758 kPa
(400 psi). or if system voltage drops below 10.5 Volts.
|
Improper condenser operation
| Improper condenser operation may result from one of the
following causes:
| • | Extremely high ambient humidity. |
| • | Insufficient air flow across condenser. |
| • | Damaged or dirty condenser fins. |
|
High side refrigerant restriction
|
- Feel liquid line before expansion tube (orifice). A cold line
indicates restriction in the high side.
- Inspect for a frost spot in order to locate the restriction.
- Repair the line as necessary.
|
Refrigerant system overcharged (high discharge and high suction pressures)
| The clutch
may cycle ON/OFF and cause compressor noise.
Recover and recharge the system with the proper amount of refrigerant.
Refer to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
|
Expansion tube
(orifice) blocked
|
- Discharge the system slowly using the low pressure service port
to prevent oil loss. Refer to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Inspect the expansion (orifice) tube for blockage. Clean or replace
the tube as required. Refer to
Expansion (Orifice) Tube Replacement
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Evacuate the system to a vacuum. Improper evacuation of the system
prior to recharge will cause air to remain in the system.
- Recharge the system with the proper amount of refrigerant. Refer
to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Leak test the system. Refer to Leak Testing
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
|
Air in system (High discharge and high suction pressures).
|
- Discharge the refrigerant system slowly using the low pressure
service port to prevent oil loss. Refer to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air
Conditioning.
- Inspect the expansion (orifice) tube for blockage. Clean or replace
the tube as required. Refer to
Expansion (Orifice) Tube Replacement
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Evacuate the system to a vacuum. Improper evacuation of the system
prior to recharge will cause air to remain in the system.
- Recharge the system with the proper amount of refrigerant. Refer
to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Leak test the system. Refer to Leak Testing
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
|
Stripped Area Diagnosis and Service
Problem
| Action
|
The compressor is damaged internally.
|
| • | If suction and discharge pressure are equal and do not change
when the A/C mode is turned ON and OFF, the compressor may be internally damaged. |
| • | Excess heat at the clutch surfaces or a free wheeling clutch driver
are signs of internal compressor damage. |
|
The expansion tube (orifice) is missing.
| Feel the liquid line after the expansion tube. If the line
is warm, discharge the system and inspect for proper installation of the
expansion tube. If the expansion tube or O-ring is missing,
replace the expansion tube. Refer to
Expansion (Orifice) Tube Replacement
in Heating, Ventilation and Air
Conditioning.
|
The refrigerant system is undercharged.
|
- The refrigerant may be undercharged when the suction pressure
is below 35 psi during the high load test.
- The suction line before the accumulator will be warm if the charge
is low.
- Add 1 lb of refrigerant.
- Recheck the pressure. Verify that the pressure is in the white
area on the chart. Then find and correct the leak.
- Evacuate the system. Refer to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air
Conditioning.
- Charge the system with the correct amount of refrigerant.
|
The expansion tube (orifice) is blocked.
|
- Discharge the system slowly using the low pressure service port
to prevent oil loss. Refer to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Inspect the expansion (orifice) tube for blockage. Clean or replace
the tube as required. Refer to
Expansion (Orifice) Tube Replacement
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Evacuate the system to a vacuum. Improper evacuation of the system
prior to recharge will cause air to remain in the system.
- Recharge the system with the proper amount of refrigerant. Refer
to Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
- Leak test the system. Refer to Leak Testing
in Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning.
|