Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
Power and Ground

and
MIL and DLC
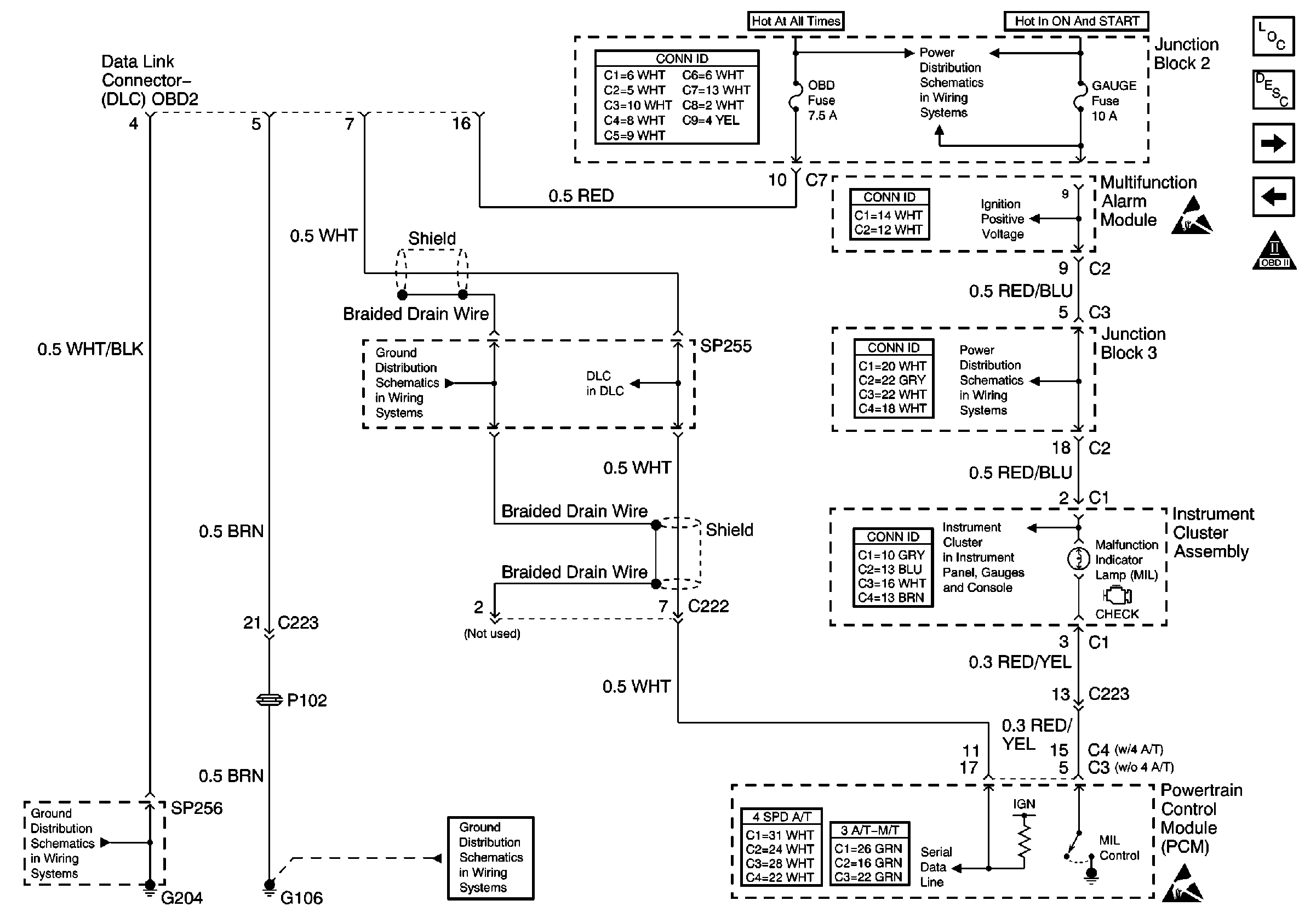
.
Description
The Powertrain OBD System Check is an organized approach to identifying a problem created by an electronic engine control system malfunction. The Powertrain OBD System Check is the starting point for any driveability concern diagnosis, because it directs the service technician to the next logical step in diagnosing the concern. Understanding the table and using it correctly will reduce diagnostic time and prevent the replacement of good parts.
DO NOT perform this check if a driveability concern is not present.
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect all the related wiring and connections for an intermittent malfunction, including the connections at the PCM. Inspect the electrical terminals for the following conditions: |
| - | Any damage |
| - | Any corrosion |
| - | Proper seating |
| • | Before proceeding to the applicable DTC table consider all of the items below: |
| - | Check for related service bulletins. |
| - | If multiple DTCs are stored, refer to the DTC tables using the following priority: |
| • | Any PCM error DTCs |
| • | Any system voltage DTCs |
| • | Any component level DTCs (sensors, switches, relays, output drivers, etc.) |
| • | Any system level DTCs (misfire, fuel trim, HO2S lean or rich, etc.) |
| - | First failures of Type B DTCs will store in Last Test Failed, but not in History. When the MIL is on and a DTC is displayed in History, a current fault is indicated. |
| - | Transmission DTCs are not located in this section. Refer to Automatic Transmission Diagnostic Information and Procedures. |
| - | If the scan tool is unable to record DTC information, then record the DTC information on paper. |
| • | For intermittents, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The OBD System Check should not be performed unless one of the concerns noted is present, failure to follow this procedure could lead to misdiagnosis of the system.
-
The MIL should be ON steady with the ignition ON and engine OFF.
-
Checking if the PCM and the scan tool can communicate.
-
This step checks if the vehicle starts.
-
Observes the DTC information. Ensures that items listed in Diagnostic Aids are considered before proceeding to the applicable DTC table.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Important:
Check for one or more of the following conditions:
Were any of the above conditions found? | -- | Go to Test Descriptions | ||||||||||||||
Is the MIL ON? | -- | |||||||||||||||
Does the scan tool display any PCM data? | -- | |||||||||||||||
Does the engine start and run? | -- | |||||||||||||||
Observe the DTC information. If DTCs are set, save the DTCs and the Freeze Frame information. Were any DTCs set? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||||
6 | Is the MIL ON, with no DTCs set? | -- | ||||||||||||||
Compare the scan tool data with the typical values shown in the Engine Scan Tool Data List. Are the displayed values normal or within typical ranges? | -- | Go to Symptoms |
