Indicators
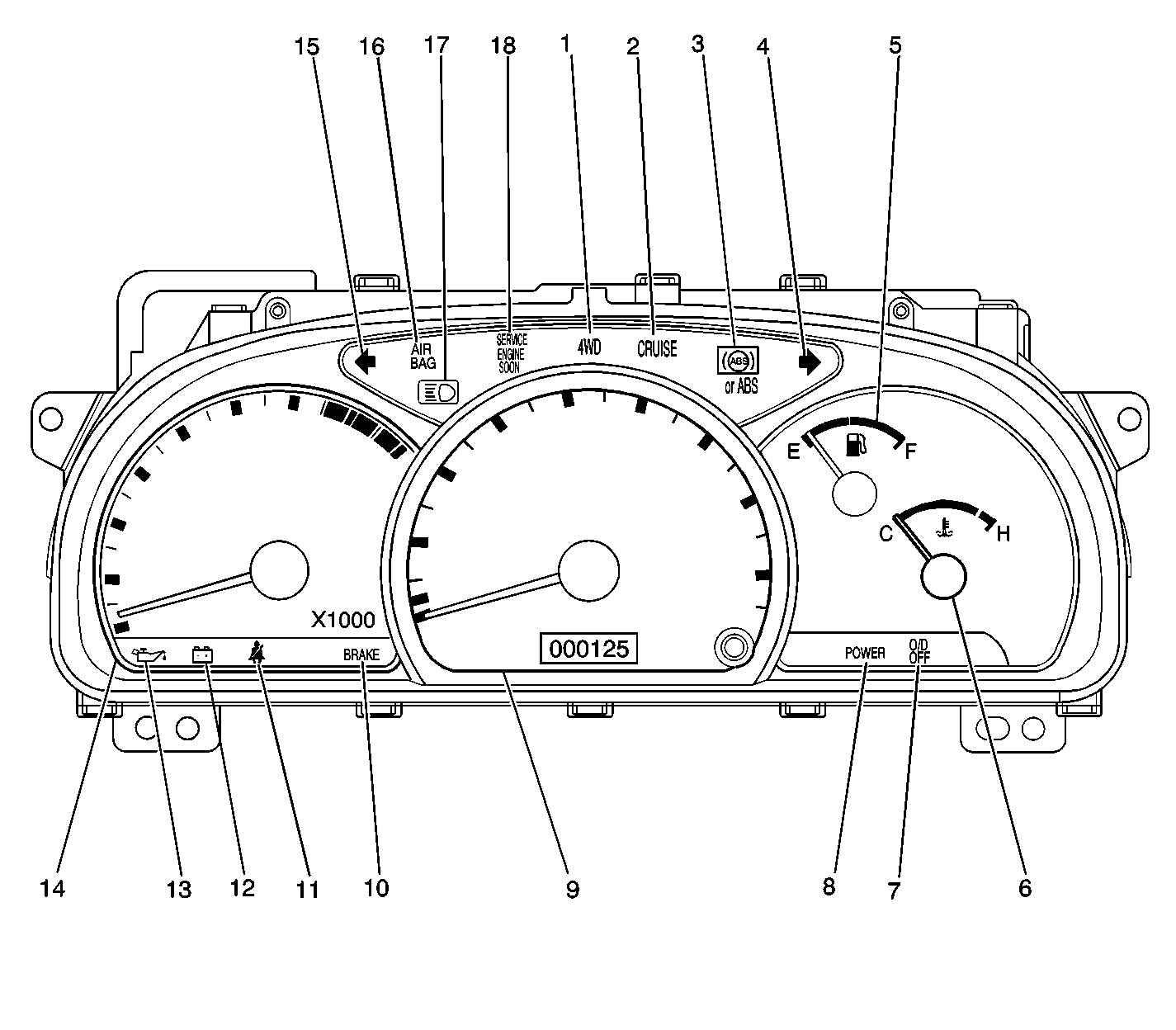
The instrument panel cluster includes the following indicators:
| • | ABS (3), if the vehicle is equipped with an antilock brake
system |
| • | CRUISE (2), if equipped |
| • | O/D OFF (7), if the vehicle is equipped with the 4-speed
A/T |
| • | POWER (8), if the vehicle is equipped with the 4-speed
A/T |
| • | SERVICE ENGINE SOON (18) |
The indicator bulbs are serviceable from the rear of the instrument
cluster. Refer to
Instrument Cluster Bulb Replacement
.
The instrument cluster indicators may differ slightly from model to
model, depending on the following factors:
| • | The transmission selection |
Display Test
Certain instrument panel cluster (IPC) features are tested when the
ignition is turned on in order to verify the features are working properly.
The following occurs at key up:
| • | The air bag indicator flashes 7 times. |
| • | The ABS indicator illuminates briefly. |
| • | The fasten seat belt indicator illuminates and stays lit until
the drivers seat belt is buckled. |
| • | These indicators stay on until the key is turned to the START
position: |
| - | The oil pressure indicator |
| - | The service engine soon indicator (MIL) |
Gages
The instrument panel cluster includes the following gages:
| • | The speedometer/odometer (9) |
| • | The engine tachometer (14) |
| • | The fuel/engine coolant temperature gage (5, 6) |
The gages are all serviceable from the instrument panel cluster. Refer
to
Speedometer Replacement
,
Tachometer Replacement
or
Fuel/Temperature Gage Replacement
for gage removal and installation
procedures.
Speedometer
Important: When replacing a speedometer or an odometer assembly, the law requires
the odometer reading of the replacement unit to be set to register the same
mileage as the prior odometer.
If the same mileage cannot be set, then the law requires the following
actions to take place:
| • | Set the replacement odometer at zero |
| • | Install a label on the driver's door frame showing the following information: |
| - | The previous odometer reading |
| - | The date of replacement |
The total mileage odometer and the two trip odometers are incorporated
into the speedometer (9). The speedometer, the total mileage odometer
and the trip odometers are serviceable only as a unit.
Odometer
Press the trip/reset switch on the cluster in order to toggle between
the total mileage odometer and the trip odometers. Press and hold the trip/reset
switch for greater than 2 seconds with either trip odometer displayed
in order to reset the trip odometer.
Engine Tachometer
The tachometer displays the engine speed in thousands of revolutions
per minute (RPM). The noise suppressor filter sends ground pulses from the
ignition system to the tachometer. The tachometer responds to the frequency
of the ground pulses, which increase with the engine speed. The purpose
of the noise suppressor filter within the circuit is to round
off pulses and remove the voltage spikes that noise in the circuit
causes.
Fuel Gage
The magnetic fields of 2 coils move the pointer of the fuel gage.
The coils are at right angles to each other. Voltage applies to coil F
from the IG fuse. The circuit divides at the opposite (ground) side
of the coil. One path seeks a ground through coil E to G103.
The other path seeks a ground through the variable resistor in the
fuel level sender.
When the fuel level is low, the resistance in the fuel level sender
is high. Current flows through coil F and coil E to ground
at G103 because current always seeks the path of the least resistance.
Because the length of the E coil winding is twice the length
of the F coil winding, the magnetic field that the E coil generates
is twice as strong as the magnetic field that the F coil generates.
The magnetic field therefore pulls the pointer to the E position.
As the fuel level increases, the resistance in the fuel level sender
decreases. Since current always seeks the path of the least resistance,
more current begins to bypass the E coil and travel directly
to ground through the fuel level sender. The coil F magnetic
field then becomes stronger than the coil E magnetic field,
causing the pointer to move toward the F position.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Gage
The magnetic field of 2 coils moves the pointer of the engine
coolant temperature (ECT) gage. The coils are at right angles to each other.
Voltage applies to the H coil from the IG fuse. The circuit divides
at the opposite (ground) side of the coil. One path seeks a ground
through coil C. The other path seeks a ground through the variable
resistor in the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sending unit.
The resistance in the ECT sending unit is high when the engine coolant
temperature is low. Current flows through the H coil and the C coil
to ground at G103 because current always seeks the path of the least
resistance. Because the length of the C coil winding is twice
the length of the coil H winding, the magnetic filed that coil C
generates is twice as strong as the magnetic field that coil H
generates. The magnetic field therefore pulls the pointer to the
C position.
As the engine coolant temperature increases, the resistance in the ECT
sending unit decreases. Since current always seeks the path of the least
resistance, more current begins to bypass the C coil and travel
directly to ground through the ECT sending unit. The coil H
magnetic field then becomes stronger than the coil C magnetic
field, causing the pointer to move toward the H position.
Oil Pressure Indicator
When the ignition switch is in the ON or START position, battery voltage
applies through the IG fuse to the oil pressure indicator in the instrument
panel cluster. If the engine oil pressure falls below 32 kPa
(4.5 psi), the oil pressure sensor that is in the engine block closes.
The closing of the switch provides a ground path to the oil pressure indicator
and the bulb lights.

