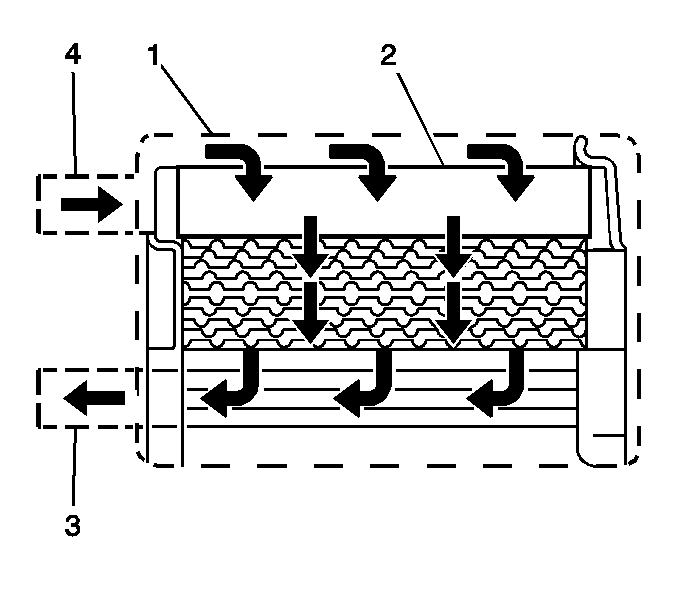
Fuel System Description Without Returnless Fuel System
Fuel System Overview
The fuel tank stores the fuel supply. The electric fuel pump supplies fuel through
an in-line fuel filter to the fuel injection system. The fuel pump provides fuel
at a higher rate of flow than is needed by the fuel injection system. The fuel pressure
regulator maintains the correct fuel pressure to the fuel injection system. A separate
pipe returns unused fuel to the fuel tank.
Fuel Tank
The fuel tank stores the fuel supply. The fuel tank is located on the left side
of the vehicle. The fuel tank is held in place by 2 metal straps that attach
to the frame. The fuel tank is molded from high density polyethylene.
Fuel Fill Pipe
The fuel fill pipe has a built-in restrictor in order to prevent refueling with
leaded fuel.
Fuel Filler Cap
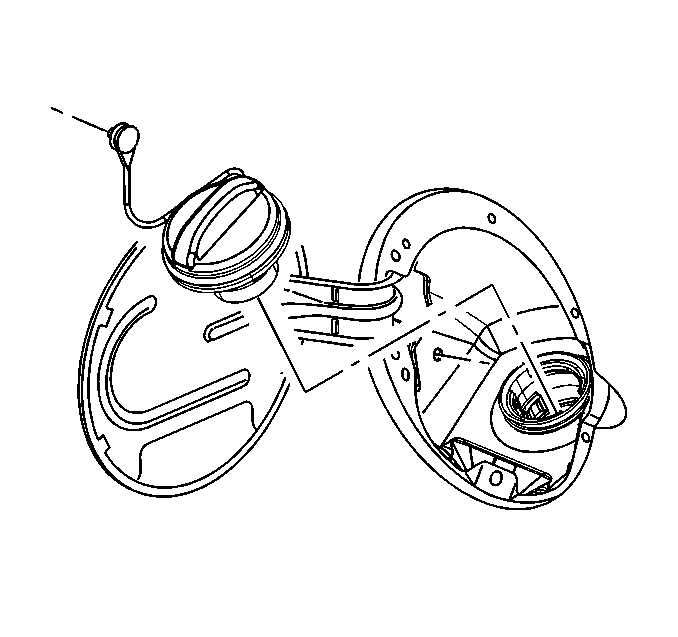
The fuel fill pipe has a tethered fuel filler cap. A torque-limiting device
prevents the cap from being over tightened. To install the cap, turn the cap clockwise
until you hear clicks. This indicates that the cap is correctly torqued and fully
seated. A built-in device indicates that the fuel filler cap is fully seated. A fuel
filler cap that is not fully seated may cause a malfunction in the emission system.
Fuel Sender Assembly
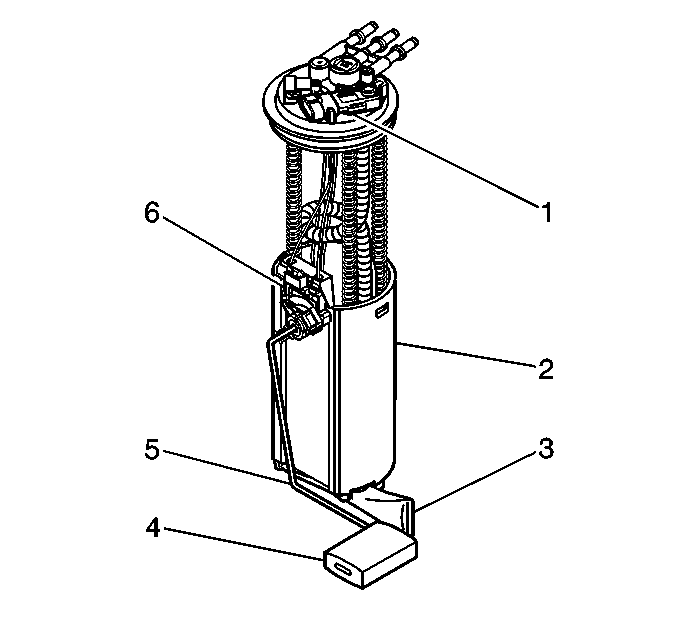
Fuel Level Sensor
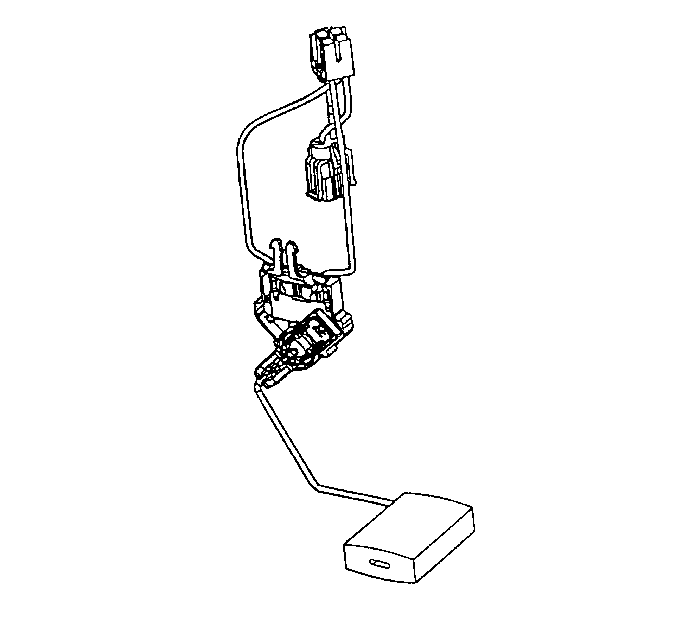
The fuel level sensor consists of a float, a wire float arm, and
a ceramic resistor cord. The position of the float arm indicates the fuel level.
The fuel level sensor contains a variable resistor, which changes resistance in correspondence
to the amount of fuel in the fuel tank. The powertrain control module (PCM) sends
the fuel level information via the class 2 circuit to the instrument panel
(I/P) cluster. This information is used for the I/P fuel gage and the low fuel warning
indicator, if applicable. The PCM also monitors the fuel level input for various diagnostics.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is mounted in the fuel sender assembly reservoir. The fuel pump
is an electric high pressure pump. Fuel is pumped to the fuel rail at a specified
flow and pressure. Excess fuel from the fuel rail assembly returns to the fuel tank
through the fuel return pipe. The fuel pump delivers a constant flow of fuel to the
engine during low fuel conditions and aggressive vehicle maneuvers. The powertrain
control module (PCM) controls the electric fuel pump operation through a fuel pump
relay. The fuel pump flex pipe acts to dampen the fuel pulses and noise generated
by the fuel pump.
Fuel Strainer
The fuel strainer attaches to the lower end of the fuel sender. The fuel strainer
is made of woven plastic. The functions of the fuel strainer are to filter contaminants
and to wick fuel. Fuel stoppage at this point indicates that the fuel tank contains
an abnormal amount of sediment.
In-Line Fuel Filter